Why the CPU is Called the Brain of the Computer?
Updated: August 23, 2024
63
In the world of computing, the Central Processing Unit (CPU) is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. This comparison is not just a metaphor; it precisely reflects the CPU’s decisive role in handling and performing a computer’s tasks. To understand why this term is used, let’s delve into what the CPU does, its essential functions, and how it compares to the brain in terms of processing and control.
Why the CPU is called the Brain of the Computer? A Detailed Comparison
What is the CPU?
Definition: The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the primary component of a computer system responsible for executing instructions from programs and applications. It is composed of millions of tiny circuits and transistors that perform billions of operations per second. Often referred to as the “processor,” the CPU reads and carries out commands from the computer’s memory.
How does the CPU help the computer?
The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is essential for a computer’s operation as it executes instructions from programs and applications.
- It performs arithmetic and logical operations
- Manages data flow between memory and peripherals
- Controls overall system functions
- By processing and interpreting commands, the CPU ensures tasks are completed efficiently
- Enable the computer to perform calculations
- Run software
- Execute complex tasks swiftly.
Essentially, the CPU acts as the brain, coordinating all computing processes.
Why is CPU most important?
The CPU is crucial because it acts as the computer’s “brain,” executing instructions from software and managing all processing tasks. It performs calculations, logical operations, and controls data flow between memory and peripherals. Without the CPU, a computer cannot process or execute any commands, making it fundamental to all computing operations. Its speed and efficiency directly impact overall system performance, making it the central component for running applications, performing calculations, and managing tasks
What is the block diagram of the CPU and explain it?
Understanding these components and their functions helps explain how the CPU processes instructions, performs calculations, and coordinates the overall operation of a computer system. CPU is the main part shown in the block diagram of computer.
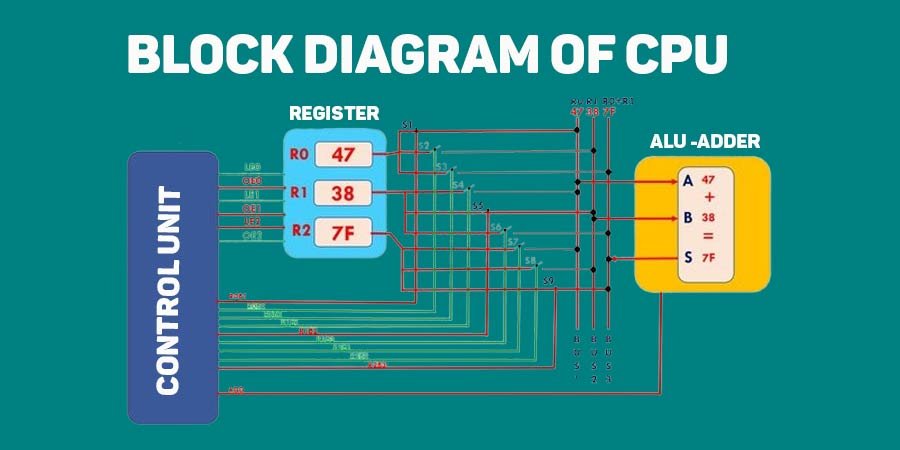
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs calculations and logical operations.
- Control Unit (CU): Directs the operation of the CPU and manages instruction execution.
- Registers: Temporary storage for data and instructions.
- Cache Memory: Fast storage for frequently accessed data.
- Bus Interface Unit (BIU): Manages communication with memory and peripherals.
- Clock: Synchronizes CPU operations.
- Instruction Register (IR): Holds the current instruction.
- Program Counter (PC): Tracks the address of the next instruction.
- Data Bus: Transfers data between CPU, memory, and peripherals.
- Address Bus: Carries addresses for data transfer.
The CPU’s Core Functions
- Fetch: The CPU retrieves instructions from the computer’s memory (RAM). This step involves fetching the instruction that the CPU needs to execute next.
- Decode: Once an instruction is fetched, the CPU decodes it to understand what action is required. This involves translating the instruction into signals that can be understood and acted upon by the CPU.
- Execute: The CPU performs the operation specified by the instruction. This could involve arithmetic calculations, data manipulation, or logical operations.
- Store: After execution, the CPU may need to store the results back into memory or send them to another component. This step ensures that the outcome of the operation is saved for future use or further processing.
Why is the CPU Compared to the Brain?
CPU is compared to brain for these four properties:
- Control and Coordination: Just as the brain controls and coordinates bodily functions, the CPU manages and orchestrates the operations of a computer. It directs the flow of data between memory, storage, and other components, ensuring that tasks are executed correctly and efficiently.
- Processing Power: The CPU’s role in processing data is akin to the brain’s role in processing information. The CPU handles complex calculations, processes data, and makes decisions based on instructions, much like how the brain processes sensory information and makes decisions.
- Decision Making: The brain makes decisions and initiates actions based on sensory inputs and cognitive processes. Similarly, the CPU executes instructions and makes decisions about which operations to perform next based on the programs it runs.
- Execution of Commands: Just as the brain sends signals to different parts of the body to execute movements or functions, the CPU sends signals to various hardware components to perform tasks such as displaying images on a screen, reading from a disk, or sending data over a network.
The Brain vs. CPU: A Comparison
- Processing Speed: The brain processes information at an incredibly fast rate, but the CPU operates at speeds measured in gigahertz (GHz), performing billions of cycles per second. This speed is essential for executing complex tasks in a fraction of a second.
- Parallel Processing: The brain can process multiple streams of information simultaneously, thanks to its complex neural networks. Modern CPUs also feature multiple cores, allowing them to perform parallel processing and handle several tasks at once.
- Learning and Adaptation: The brain learns and adapts through experience, which contributes to cognitive development. While traditional CPUs do not “learn” in the same way, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are enabling processors to adapt and improve their performance over time.
Conclusion
The analogy of the CPU as the “brain” of the computer captures its pivotal role in controlling and managing the operations of a computer system. We have read about it in the characteristics of computer. By fetching, decoding, executing, and storing instructions, the CPU orchestrates the flow of information and ensures that tasks are performed efficiently. Just as the brain is central to cognitive functions and decision-making in humans, the CPU is central to the functionality and performance of a computer. Understanding this comparison highlights the importance of the CPU in computing and underscores its critical role in modern technology
Please Write Your Comments