What is the Difference between SSD and HDD? Facts Revealed
Updated: September 4, 2024
62
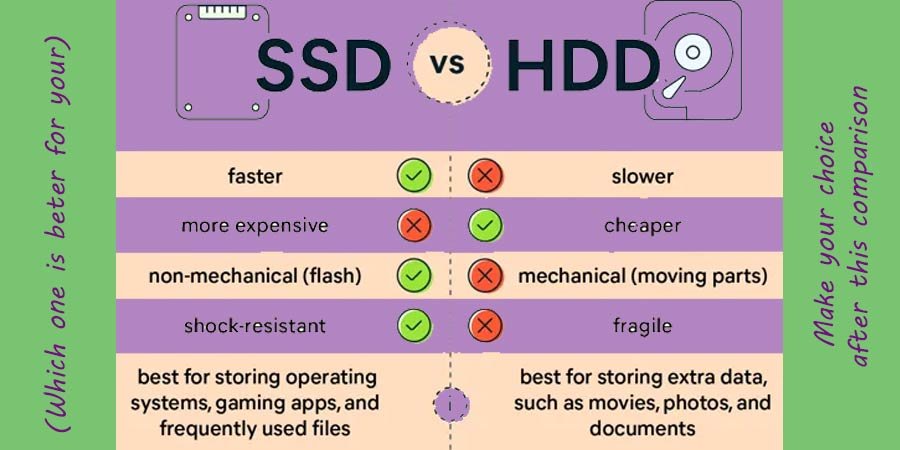
In the realm of data storage, Solid State Drives (SSD) and Hard Disk Drives (HDD) are the two primary types of storage devices. SSDs use flash memory to store data, which provides faster access times and greater durability due to the lack of moving parts.
Conversely, HDDs use spinning magnetic disks to read and write data, which can be slower but offers larger storage capacities at a lower cost. Understanding the differences between these two types of drives is crucial for making informed decisions about which storage solution best meets your needs.

What is the Difference between SSD and HDD? Facts Revealed
1. HDD VS SSD Speed and Performance
One of the most significant differences between SSDs and HDDs is their speed. SSDs are considerably faster than HDDs. This is due to the fact that SSDs use NAND flash memory, which allows for near-instantaneous access to data. HDDs, on the other hand, rely on mechanical parts such as spinning disks and moving read/write heads which can cause latency.
CPU plays a pivotal role in making computer fast. CPU is called the brain of computer. This mechanical nature limits the speed at which data can be accessed and written. As a result, SSDs offer faster boot times, quicker file transfers, and more responsive applications compared to HDDs.
2. SSD VS HDD lifespan and Reliability
Durability is another area where SSDs outperform HDDs. SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them more resilient to physical shock and vibrations. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for portable devices like laptops and external drives.
HDDs, with their spinning disks and moving parts, are more susceptible to damage from physical impacts or drops. Additionally, the wear and tear on mechanical components can lead to a higher likelihood of failure over time compared to the more robust SSDs.
3. Difference between SSD and HDD Storage Capacity
Memory or storage is one of the basic operations performed by the computer. When it comes to storage capacity, HDDs typically offer more space at a lower cost. HDDs can be found with capacities ranging from hundreds of gigabytes to several terabytes, making them a popular choice for bulk storage needs, such as for large media files and extensive databases.
While SSDs have been catching up in terms of capacity, they are still generally more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. For users who need vast amounts of storage without breaking the bank, HDDs remain the more cost-effective option.
4. Which is cheaper, HDD or SSD?
The cost of SSDs and HDDs reflects their differences in performance and capacity. SSDs are generally more expensive per gigabyte than HDDs. This higher cost is attributed to the advanced technology and faster speeds that SSDs provide.
HDDs, with their older technology and larger storage capacities, offer a more budget-friendly solution for users who need large amounts of storage without requiring high-speed performance. As SSD prices continue to decrease, the gap between SSD and HDD costs is narrowing, but HDDs still hold a price advantage for high-capacity needs.
5. Power Consumption
Power consumption is another key factor where SSDs have an edge over HDDs. SSDs consume less power because they do not have moving parts, which leads to better energy efficiency. This is particularly advantageous for mobile devices like laptops, where longer battery life is a priority.
HDDs, with their mechanical components, require more power to operate, which can lead to shorter battery life and higher energy costs over time. Power consumption is one of the main characteristics of computer.
6. Noise Levels
In terms of noise, SSDs have a clear advantage. Since they lack moving parts, SSDs operate silently. HDDs, due to their spinning disks and moving read/write heads, can generate noticeable noise during operation. This noise can be particularly distracting in quiet environments or in settings where minimal disruption is desired.
7. Fragmentation
File fragmentation is a concept more relevant to HDDs than SSDs. As files are written and deleted on an HDD, they can become fragmented, meaning pieces of the same file are scattered across different locations on the disk. This fragmentation can slow down read and write speeds as the read/write head has to move to different areas to access the complete file.
SSDs do not suffer from fragmentation in the same way because their flash memory allows for uniform access speeds regardless of where the data is stored on the drive.
Conclusion
In summary, SSDs and HDDs each have their strengths and weaknesses. SSDs offer superior speed, durability, and energy efficiency, making them ideal for high-performance needs and portable devices. HDDs, however, provide larger storage capacities at a lower cost, making them suitable for bulk storage applications.
Your choice between SSD and HDD will largely depend on your specific needs regarding performance, capacity, and budget. As technology evolves, the distinctions between these two types of drives may continue to shift, but understanding their current differences will help you make the best choice for your data storage requirements.
Frequently Asked Question
Which lasts longer SSD or HDD?
SSDs generally last longer than HDDs in terms of operational lifespan. SSDs, with no moving parts, are less prone to mechanical failure and physical damage. They use flash memory that can endure a significant number of read/write cycles before wearing out. HDDs, however, rely on spinning disks and moving read/write heads, which can wear out over time and are susceptible to physical shocks. While SSDs may have a limited number of write cycles, their overall durability tends to surpass that of HDDs.
Can I have both SSD and HDD in laptop?
Yes, you can have both an SSD and an HDD in a laptop. Many laptops, especially those designed for high performance or gaming, come with dual-drive configurations.The SSD is typically used for the operating system and frequently accessed applications to benefit from its speed, while the HDD provides additional storage space for files, media, and less critical data. This combination leverages the speed of the SSD and the larger capacity of the HDD, offering a balanced approach to performance and storage.
How many HDD is equal to SSD?
The equivalence of HDDs to SSDs depends on storage capacity. For instance, a single 1TB SSD typically equals a 1TB HDD in terms of storage space. However, to match the performance of a 1TB SSD, you might need multiple HDDs, as SSDs provide faster data access speeds and better overall performance compared to HDDs.
What is SSD and HDD full form?
- SSD stands for Solid State Drive
- HDD stands for Hard Disk Drive
What is the best SSD for a laptop?
The Samsung 970 EVO Plus is widely regarded as one of the best SSDs for laptops due to its high speed, reliability, and overall performance. For a more budget-friendly option, the Crucial MX500 offers great value with solid performance and durability.
What are the disadvantages of SSD?
The main disadvantages of SSDs include higher cost per gigabyte compared to HDDs, limited write endurance over time, and generally lower storage capacities. Additionally, SSDs can be more expensive upfront, which might not be ideal for users needing extensive storage on a tight budget.
How many GB SSD is good for a laptop?
A 500GB SSD is generally a good balance for most laptops, providing ample space for the operating system, applications, and files. For heavy users or those with large media libraries, a 1TB SSD might be more appropriate.
Can I replace HDD with SSD in laptop?
Yes, you can replace an HDD with an SSD in a laptop. This upgrade improves performance, speed, and reliability. Ensure compatibility and back up your data before making the switch.
Please Write Your Comments